주요 내용
- Authentication 과 ServiceAccount 에 대한 이해
- RBAC plugin, Role/RoleBinding, ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding 에 대한 이해
12.1 Understanding authentication
API server 가 요청을 받게 되면, authentication plugin 을 거치며 요청을 보낸 주체가 누구인지 분석한다.
Plugin 을 거치게 되면 username, user ID, 클라이언트가 속하는 group 등의 정보가 API server 에게 전달된다.
12.1.1 Users and groups
Understanding users
Kubernetes 에서는 API server 에 연결하는 주체를 2가지로 분류한다.
- 사람 (users)
- Pods (정확히는 pod 내에 실행 중인 어플리케이션)
실제 사람과 같은 경우 외부 시스템 (SSO 등) 에 의해 관리된다. (관심 대상이 아니다) 실제 사용자의 계정을 관리하는 리소스는 존재하지 않는다.
한편 pod 의 경우 service accounts 를 사용하는데, 이는 클러스터에 ServiceAccount 리소스로 저장된다.
Understanding groups
모든 사용자는 하나 혹은 그 이상의 group 에 속할 수 있다. Group 을 사용하게 되면 여러 명의 user 에게 동시에 권한을 줄 수 있다.
Authentication plugin 에서 group 을 알려준다고 했는데, plugin 은 group 을 string 으로 알려준다. 몇 가지의 내장된 group 이 있다.
system:unauthenticated: 모든 authentication plugin 이 요청을 authenticate 할 수 없는 경우system:authenticated: Authentication 이 성공한 user 에게 자동으로 설정된다system:serviceaccounts: 시스템(클러스터)에 존재하는 모든 ServiceAccounts 를 포함한다system:serviceaccounts:<namespace>: 특정 namespace 안의 모든 ServiceAccounts 를 포함한다
12.1.2 Introducing ServiceAccounts
Pod 가 API server 와 통신할 때는 /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token 에 있는 token 을 이용해서 authentication 한다는 것을 배웠다. (이 파일은 secret volume 을 통해 mount 된다) 이제 이 파일이 정확히 무엇을 의미하는지 알아본다.
모든 pod 는 ServiceAccount 와 연결되게 되는데, 이 token 파일에는 ServiceAccount 의 authentication token 이 들어있다. 그래서 어플리케이션이 token 을 이용해서 API server 와 통신하게 되면, authentication plugin 에서는 해당 ServiceAccount 를 authenticate 하고, API server 에게 ServiceAccount username 을 알려준다.
ServiceAccount username 은 다음과 같은 형식으로 구성되어 있다.
system:serviceaccount:<namespace>:<service account name>이제 API server 는 이 ServiceAccount username 을 authorization plugin 에게 넘기고, 요청의 action 을 수행할 권한이 있는지 확인한다.
결국 ServiceAccount 는 pod 내의 어플리케이션이 API server 와의 통신에서 자신을 authenticate 하는 방법이다.
Understanding the ServiceAccount resource
ServiceAccount 도 namespace 에 귀속된다.
각 namespace 에는 default ServiceAccount 가 기본적으로 생성되며, pod 들은 이 default ServiceAccount 를 기본적으로 사용한다.
$ kubectl get sa
NAME SECRETS AGE
default 1 79d각 pod 는 오직 하나의 ServiceAccount 와 연결될 수 있지만, 같은 ServiceAccount 를 여러 pod 에서 재사용 할 수 있다. 단 제약 조건이 있는데, 같은 namespace 의 ServiceAccount 만 사용할 수 있다.
Understanding how ServiceAccounts tie into authorization
Pod manifest 에 ServiceAccount 를 지정하게 되는데, (지정하지 않으면 default 사용) ServiceAccount 마다 역할이 정해져 있기 때문에 pod 의 권한 또한 제어가 가능하다.
API server 가 token 을 받으면 어떤 ServiceAccount 인지 확인하고, 해당 ServiceAccount 의 권한을 확인하여 요청을 수행할 권한이 있는지 확인하게 되는 방식이다.
12.1.3 Creating ServiceAccounts
권한 부여는 최소로 하는 것이 원칙이다. 그래서 pod 의 용도에 맞게 ServiceAccount 를 직접 설정하고 pod 에 연결해야한다.
생성은 아래와 같이 하면 된다.
$ kubectl create serviceaccount <NAME>이제 describe 로 확인해 보면,
$ kubectl describe sa foo
Name: foo
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Image pull secrets: <none>
Mountable secrets: foo-token-hnx6x
Tokens: foo-token-hnx6x
Events: <none>Tokens: ... 에 새로운 token이 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있고, 이는 Secret 으로 관리된다.
Mountable secrets
원래 pod 는 원하는 Secret 을 임의로 mount 할 수 있다. 하지만 pod 의 ServiceAccount 에서, 이 ServiceAccount 를 사용하는 pod 이 mount 할 수 있는 Secret 을 제한할 수 있다.
Mountable secrets 목록은 이 pod 가 mount 할 수 있는 Secret 의 목록이다. 다른 Secret 은 사용할 수 없다.
Image pull secrets
Image pull secret 은 private image repository 에서 image 를 pull 받을 때 사용하는 credential 이다. Mountable secrets 처럼 사용 가능한 secret 을 제한하는 것은 아니고, image pull secret 에 있는 secret 은 해당 ServiceAccount 를 사용하는 모든 pod 에 자동으로 mount 된다.
12.1.4 Assigning a ServiceAccount to a pod
Pod definition 에서 .spec.serviceAccountName 필드에 적어주면 된다. Pod 생성할 때 미리 정해야 하며, pod 가 생성된 뒤에는 수정할 수 없다.
12.2 Securing the cluster with role-based access control
Role-based access control (RBAC) plugin 을 사용하게 되면, unauthorized user 가 클러스터의 상태를 조회하거나 수정하는 것을 막을 수 있다. RBAC 를 사용하여 클러스터의 authorization 을 관리하는 방법을 살펴본다.
12.2.1 Introducing the RBAC authorization plugin
Kubernetes API server 는 authorization plugin 을 사용해서 요청을 보낸 주체가 작업(action)을 수행할 수 있는지 판단한다고 했다.
Understanding actions
작업의 종류에는 다음과 같은 것들이 있다. 기본적으로는 HTTP 요청을 사용하기 때문에 GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등이 있고, 위 요청을 하면서 특정 리소스의 정보를 요구하게 된다. 예를 들면 pod 의 목록 가져오기 (GET), Service 생성하기 (POST), Secret 업데이트 (PUT) 등과 같은 요청이 있을 것이다.
이제 RBAC 와 같은 authorization plugin 을 사용하게 되면, 클라이언트가 리소스에 대한 요청을 할 수 있는지 없는지 판단하게 된다. (리소스의 종류와 작업의 종류 별도로 관리 가능)
추가로 RBAC 의 경우, 리소스의 특정 인스턴스 (특정 이름을 가진 service)에 대해서도 권한을 관리할 수 있게 된다.
Understanding the RBAC plugin
RBAC plugin 은 user 의 role 을 기반으로 authorization 을 하게 된다. User (사용자/ServiceAccount) 는 하나 이상의 role 이 부여되며, 각 role 마다 어떤 리소스에 어떤 작업을 할 수 있는지 정해져 있다.
만약 user 가 다수의 role 을 부여받았다면, role 에서 부여한 권한들의 합집합이 user 의 권한이 된다.
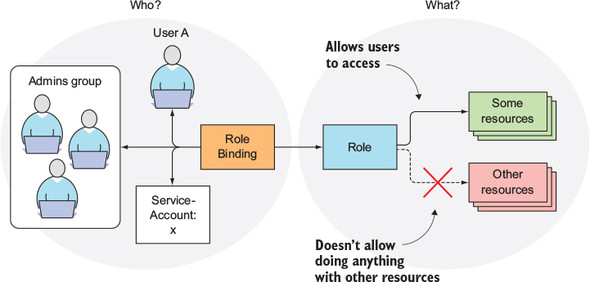
12.2.2 Introducing RBAC resources
RBAC authorization rules 은 4개의 리소스를 통해 설정된다. 크게 2가지 분류로 나뉜다.
- Role 과 ClusterRole: 어떤 리소스에 어떤 작업을 수행할 수 있는지 관리한다
- RoleBinding 과 ClusterRoleBinding: 위 role 을 적용할 user, group, ServiceAccounts 를 관리한다
Roles 는 무엇(what)을 할 수 있는지 관리하는 것이고, bindings 는 누가(who)할 수 있는지 관리한다.
그리고 Cluster 가 붙은 리소스의 차이점은 Role/RoleBinding 는 namespace 가 존재하는 리소스를 관리하는 반면, ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding 의 경우 namespace 가 없는 클러스터 레벨의 리소스를 관리한다는 점이다.
Creating the namespaces and running to pods
Namespace 별로 동작이 달라지는 것을 확인하기 위해 namespace 를 만든다.
$ kubectl create ns foo
$ kubectl run test --image=luksa/kubectl-proxy -n foo
$ kubectl create ns bar
$ kubectl run test --image=luksa/kubectl-proxy -n bar이제 터미널을 2개 열고 각 pod 안으로 들어간다.
$ kubectl exec -it test -n foo -- sh
$ kubectl exec -it test -n bar -- shListing services from your pods
RBAC 가 동작하고 있음을 확인하기 위해 curl 을 사용해 foo namespace 의 Service 목록을 가져올 것이다.
/ # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/foo/services
{
"kind": "Status",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
},
"status": "Failure",
"message": "services is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:foo:default\" cannot list resource \"services\" in API group \"\" in the namespace \"foo\"",
"reason": "Forbidden",
"details": {
"kind": "services"
},
"code": 403
}Default ServiceAccount 에는 아무 권한이 주어져 있지 않으므로 실패해야 한다. RBAC 가 잘 동작하고 있다.
12.2.3 Using Roles and RoleBindings
Creating Roles
이제 Role 을 생성해보자. Service 목록을 조회할 수 있도록 할 것이다.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: foo # Role 은 namespaced resource 이다
name: service-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # Service 는 core apiGroup 에 있는 리소스이다
verbs: ["get", "list"] # 특정 리소스를 get 하는 요청, 전체를 list 하는 요청 허용
resources: ["services"] # 대상 리소스는 service 이고, 반드시 복수형으로 적어야 한다리소스를 명시할 때 반드시 복수형으로 적어야 한다. 그리고 리소스의 특정 인스턴스에만 접근을 허용하고 싶을 경우
resourceNamesfield 를 적어주면 된다.
생성은 마찬가지로 YAML 파일을 POST 하면 되고, namespace 에 주의해야 한다.
$ kubectl create -f service-reader.yaml -n fooRole 을 생성하는 또 다른 방법으로 CLI 에 직접 입력하는 방법이 있다. bar namespace 에는 CLI 로 생성한다.
$ kubectl create role service-reader --verb=get --verb=list \
--resource=services -n barBinding a role to a ServiceAccount
이제 이 Role 을 ServiceAccount 에 bind 해줘야 Role 이 실제로 적용된다. RoleBinding 리소스를 생성한다.
$ kubectl create rolebinding test --role=service-reader \
--serviceaccount=foo:default -n fooUser 에게 bind 하려면
--user, group 에게 bind 하려면--group옵션을 주면 된다.
RoleBinding 은 하나의 Role 만 reference 할 수 있다. 다만 Role 자체는 재사용이 가능하므로 여러 RoleBinding 을 생성할 수 있다.
이제 foo 의 default ServiceAccount 에 service-reader Role 이 bind 되었다. Service 의 목록을 다시 조회해 본다.
/ # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/foo/services
{
"kind": "ServiceList",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "812515"
},
"items": []
}조회가 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Including ServiceAccounts from other namespaces in a RoleBinding
현재 namespace bar 에 생성한 pod 내에서는 Service 목록을 조회할 수 없다. RoleBinding 을 수정해보자.
$ kubectl edit rolebinding test -n foo그리고 아래와 같이 수정한다.
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: foo
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: bar그러면 이 RoleBinding 이 bar namespace 의 default ServiceAccount 에도 적용되고, bar 안의 pod 에서 foo namespace 의 Service 목록을 조회할 수 있다. 다만, 여전히 bar namespace 의 Service 목록은 조회가 불가능하다.
12.2.4 Using ClusterRoles and ClusterRoleBindings
ClusterRole 과 ClusterRoleBinding 을 사용하면 클러스터 레벨의 리소스에 대한 권한을 관리할 수 있게 된다.
Role 의 경우 Role 이 존재하고 있는 namespace 안의 리소스에 대한 권한만 부여할 수 있다. (위 예시에서 bar namespace 의 pod 가 foo namespace 의 Service 를 조회했지만, 이는 부여된 Role 이 foo namespace 에 속해 있기 때문) 그래서 만약 여러 namespace 에 접근해야 한다면, 각 namespace 마다 Role 과 RoleBinding 을 하나씩 전부 만들어줘야 한다.
추가로 Node, PV, Namespace 리소스의 경우 애초에 namespace 가 존재하지 않기도 하고, API server 의 endpoint 중 리소스를 나타내고 있지 않은 URL (/healthz) 도 있기 때문에 Role 만 사용해서는 위와 같은 정보를 API server 에 요청할 수 없게 된다.
ClusterRole 은 클러스터 레벨의 리소스로, namespace 가 없는 리소스나 리소스가 아닌 URL 에 대한 접근 권한을 관리할 수 있게 해준다. 또는 여러 namespace 에서 사용할 공통적인 권한을 정할 때도 사용한다.
Allowing access to cluster-level resources
우선 ClusterRole 을 생성해 본다. Namespace 가 없음에 유의한다.
$ kubectl create clusterrole pv-reader --verb=get,list \
--resource=persistentvolumesClusterRole 을 bind 하기 전에 권한이 있는지 확인해보자.
/ # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/persistentvolumes
{
"kind": "Status",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
},
"status": "Failure",
"message": "persistentvolumes is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:foo:default\" cannot list resource \"persistentvolumes\" in API group \"\" at the cluster scope",
"reason": "Forbidden",
"details": {
"kind": "persistentvolumes"
},
"code": 403
}요청이 실패한다. 이제 ClusterRoleBinding 을 생성한다. 마찬가지로 namespace 가 없음에 유의한다.
클러스터 레벨의 리소스에 대해 권한을 관리하려면 반드시 ClusterRoleBinding 을 이용해야 한다.
$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding pv-test --clusterrole=pv-reader \
--serviceaccount=foo:default이제 다시 요청해 보면 성공하는 것이 확인된다.
Allowing access to non-resource URLs
리소스를 reference 하지 않는 URL 에 대한 요청 권한도 직접 허용해야 한다. 대부분의 경우 system:discovery 라는 이름의 ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding 이 존재하여 이를 해결해준다.
다음은 kubectl get clusterrole system:discovery -o yaml 의 output 이다.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
creationTimestamp: "2021-03-17T15:34:10Z"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
managedFields:
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.: {}
f:rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: {}
f:labels:
.: {}
f:kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: {}
f:rules: {}
manager: kube-apiserver
operation: Update
time: "2021-03-17T15:34:10Z"
name: system:discovery
resourceVersion: "76"
uid: a752c732-0544-455c-8c63-968ab2da0351
rules:
- nonResourceURLs: # 리소스를 참조하지 않는 URL 목록
- /api
- /api/*
- /apis
- /apis/*
- /healthz
- /livez
- /openapi
- /openapi/*
- /readyz
- /version
- /version/
verbs: # GET 만 허용된다
- get마찬가지로 ClusterRoleBinding 도 확인해본다. kubectl get clusterrolebinding system:discovery -o yaml 의 output 이다.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
creationTimestamp: "2021-03-17T15:34:10Z"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
managedFields:
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.: {}
f:rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: {}
f:labels:
.: {}
f:kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: {}
f:roleRef:
f:apiGroup: {}
f:kind: {}
f:name: {}
f:subjects: {}
manager: kube-apiserver
operation: Update
time: "2021-03-17T15:34:10Z"
name: system:discovery
resourceVersion: "138"
uid: 2942e213-29be-4ecb-8439-be3167c1177b
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:discovery
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: system:authenticated마지막 subjects 를 보면 system:authenticated group 에 bind 되어있는 것을 확인할 수 있다. Authenticated user 라면 ClusterRole 의 적용을 받는다.
그래서 로컬 머신에서 curl 요청을 보내면 실패하게 된다.
$ curl https://$(minikube ip):8443/api -k
{
"kind": "Status",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
},
"status": "Failure",
"message": "forbidden: User \"system:anonymous\" cannot get path \"/api\"",
"reason": "Forbidden",
"details": {
},
"code": 403
}Using ClusterRoles to grant access to resources in specific namespaces
ClusterRole 이 반드시 ClusterRoleBinding 과 연결된 필요는 없다. Namespace 가 존재하는 RoleBinding 과도 연결될 수 있다.
view 라는 ClusterRole 을 살펴본다. kubectl get clusterrole view -o yaml 중 일부이다.
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- configmaps
- endpoints
- persistentvolumeclaims
- persistentvolumeclaims/status
- pods
- replicationcontrollers
- replicationcontrollers/scale
- serviceaccounts
- services
- services/status
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
...자세히 보면 ConfigMap, Endpoints, PVC, Pods 와 같이 namespace 된 리소스들이 적혀있다.
이러한 경우 ClusterRole 이 RoleBinding/ClusterRoleBinding 중 어느 쪽과 연결되느냐에 따라 권한이 달라진다. 만약 RoleBinding 에 연결하게 되면, RoleBinding 은 namespace 가 있으므로 RoleBinding 의 namespace 안에 있는 리소스에 권한이 부여된다. 반면 ClusterRoleBinding 을 사용하게 되면 임의의 namespace 안에 있는 리소스에 대해 권한이 부여된다.
Summary
| 접근 | Role Type | Binding Type |
|---|---|---|
| 클러스터 레벨 리소스 | ClusterRole |
ClusterRoleBinding |
| 리소스를 참조하지 않는 URL | ClusterRole |
ClusterRoleBinding |
| 임의의 namespace 에서 namespace 가 있는 리소스 접근 | ClusterRole |
ClusterRoleBinding |
| 특정 namespace 에서 namespace 가 있는 리소스 접근 (ClusterRole 을 재사용하는 경우) | ClusterRole |
RoleBinding |
| 특정 namespace 에서 namespace 가 있는 리소스 접근 (각 namespace 에 Role 생성) | Role |
RoleBinding |
12.2.5 Understanding default ClusterRoles and ClusterRoleBindings
Kubernetes 에는 기본적으로 설정되어 있는 ClusterRole 과 ClusterRoleBinding 이 있다. API server 가 시작될 때 매 번 업데이트 되기 때문에 실수로 삭제하는 경우 role 이 꼬이는 것을 방지하고, Kubernetes 가 업데이트 될 때 같이 업데이트 된다.
중요한 ClusterRole 몇 가지만 살펴본다.
Allowing read-only access to resources with view ClusterRole
이 ClusterRole 은 namespace 가 존재하는 대부분의 리소스를 조회 (view) 할 수 있다. 다만 Role, RoleBinding, Secret 은 제외되는데, 이는 privilege escalation 을 막기 위함이다. 어떤 secret 는 더 많은 권한을 가지고 있을 수도 있다.
Allowing modifying resources with edit ClusterRole
말 그대로 수정을 하게 해준다. 이 경우 Secret 도 접근하여 수정할 수 있지만, Role, RoleBinding 은 여전히 제외된다. 이 또한 privilege escalation 을 방지하기 위함이다.
Full control of a namespace with admin ClusterRole
Namespace 에 속한 모든 리소스를 읽고 변경할 수 있다. 다만 ResourceQuota 와 Namespace 자체는 건드릴 수 없다. 앞의 edit ClusterRole 과의 차이점은 Role, RoleBindings 를 읽고 쓸 수 있다는 점이다.
Privilege escalation 을 막기 위해서 한 사용자가 Role 을 업데이트 하는 경우, 그 사용자가 업데이트 하려는 Role 에 정의된 모든 권한을 가지고 있는지 확인한다. 당연히 권한의 범위 (namespace) 도 동일해야 한다. 가지고 있어야만 수정할 수 있다.
Complete control with cluster-admin ClusterRole
모든 권한이 주어진다!
Other ClusterRoles
system: 으로 시작하는 ClusterRole 들은 Kubernetes 컴포넌트들이 사용한다. kube-scheduler (Scheduler 가 사용), node (Kubelet 이 사용), controller: 등등이 있다.
12.2.6 Granting authorization permissions wisely
- Principle of least privilege 만 기억하면 된다. 권한은 최소한으로 준다.
- 각 pod 마다 ServiceAccount 를 생성하는 것이 바람직하다.
'Computer Science > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 15. Automatic scaling of pods and cluster nodes (0) | 2021.07.18 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 14. Managing pods' computational resources (0) | 2021.07.11 |
| Chapter 13. Securing cluster nodes and the network (0) | 2021.06.29 |
| Chapter 11. Understanding Kubernetes internals (0) | 2021.05.30 |
| Chapter 10. StatefulSets: deploying replicated stateful applications (0) | 2021.05.17 |
| Chapter 9. Deployments: updating applications declaratively (0) | 2021.04.30 |




댓글